Li group-李彦光课题组
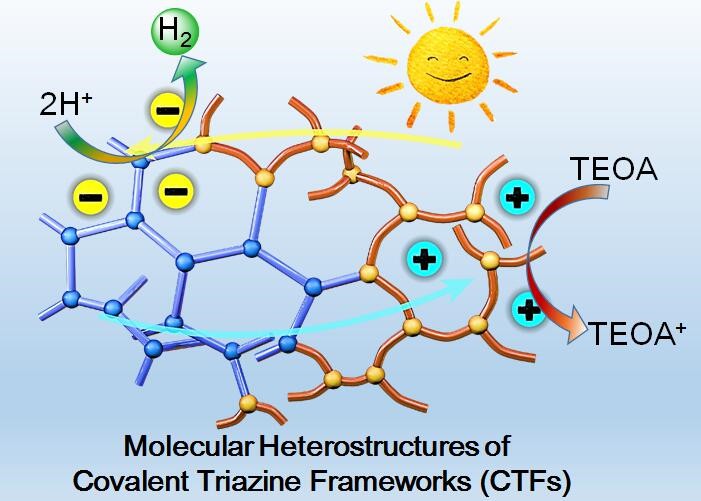
研之成理:共价三嗪框架材料分子异质结提升光催化产氢效率
本文采用逐步聚合方法选择性地将供电子和吸电子基团选择性地引入聚合物骨架中,构筑了纯有机、共价连接的三嗪框架(CTFs)材料分子异质结。由于两种聚合物半导体之间的能级差异,能够促使光生载流子在聚合物界面的传递和分离,有效抑制其复合,从而提高光催化效率。
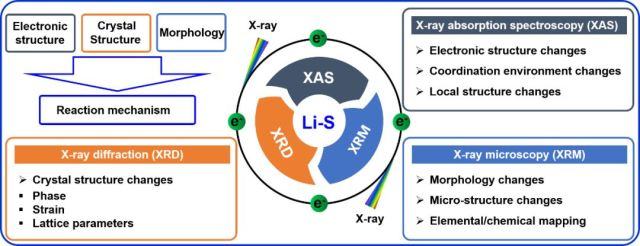
研之成理:基于同步辐射的原位表征技术对锂-硫电池反应机理的研究
近日,苏州大学功能纳米与软物质研究院(FUNSOM)的张亮教授课题组和李彦光教授课题组以“Deciphering the reaction mechanism of lithium-sulfur batteries by in-situ/operando synchrotron-based characterization techniques”为题在 Adv. Energy Mater. 期刊上发表综述文章,总结了利用同步辐射的原位表征技术来研究锂硫电池反应机理的最新研究进展。
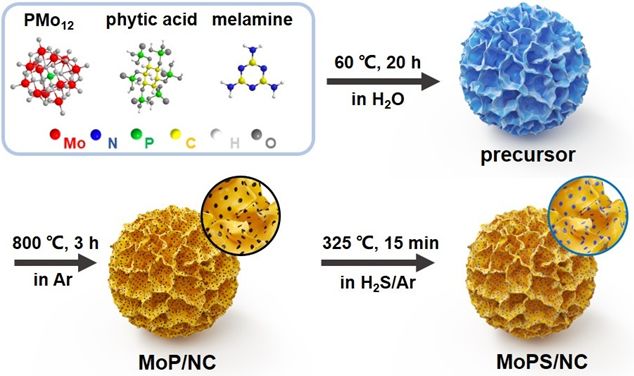
研之成理:多级碳骨架支撑的超分散磷化钼/磷硫化钼纳米颗粒电催化析氢
目前,人们对析氢电催化材料的发展兴趣已逐渐从贵金属材料转移到具有类似催化活性且成本更加低廉的非贵金属基替代品上了。这之中的佼佼者——过渡金属磷化物,自2013年被发现具有析氢催化活性至今,已成为了最好的非贵金属基析氢电催化剂之一。
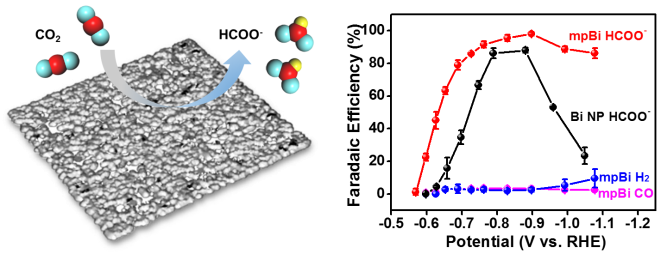
Materials Views - China: “铋”不可少的电催化还原CO2
光合作用是指绿色植物在光照条件下将二氧化碳(CO2)和水转化成富能的有机物并释放出氧气的过程。它不仅完成了物质转化(无机物到有机物)、能量转化(光能到化学能),同时也维系了生物圈的碳氧平衡。

Chem: Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide
In the October issue of Chem, Han et al. reported that the recycling of carbon dioxide (CO2) for use as fuels and chemicals can be achieved by a combination of nanotechnology and molecular engineering to give robust, active, and selective organic-inorgani

能源学人:利用金属铜集流体实现多硫化物活性材料的化学固硫和转化:一种获得室温Li-S和Na-S电池的新方法
传统锂离子电池的性能已经接近其所能达到的极限,无法满足未来社会对高能量密度的需求。近年来,室温金属-硫(例如Li/Na-S)电池的研究热度居高不下。正极材料S具有高达1672mAh/g的理论容量,丰富的自然储量,以及低廉的价格,因此被认为是最具有潜力的下一代电池体系。

苏州大学&美国阿贡国家实验室:非晶MoS3作为室温条件下Li-S和Na-S电池硫当量正极材料
目前Li-S和Na-S电池存在的问题主要是其电池反应中存在多硫中间体,尽管近年来人们不断致力于在负极表面上修饰各种功能材料,以捕获聚硫化物减少影响,但仍旧无法彻底解决这一问题。开发具有高性能、高容量、高稳定性同时电极反应中少有甚至不产生中间多硫化物的负极电极材料成为目前硫电池领域的重要发展需求。

X-MOL: Chem--基于聚酞菁钴和碳纳米管复合材料的电催化CO2还原
人类社会特别是到了近代工业社会以后,生产生活需要消耗大量能源,对煤、石油等化石能源的依赖达到了新的高度,使地球上“碳”的存在形式发生了改变。原来埋藏在地下的煤和石油,属于“地下碳库”,燃烧之后以CO2的形式排向大气,致使地层中沉积碳库的碳以较快的速度流向“大气碳库”。

Materials Views - China: 直接乙醇燃料电池阳极催化剂的“一剂良药”
由于日益严重的能源和环境问题,新一代绿色能源的研究与推广变得越来越紧迫。乙醇作为液体燃料具有能量密度高、便于储存和运输、来源广泛、绿色环保等优点。因此直接乙醇燃料电池吸引了广泛关注,相关研究方兴未艾。

Materials Views - China: 二氧化碳还原:从电催化到光催化
能源短缺和环境污染是人类社会发展面临的最严峻的问题。当前世界的能源消耗仍是以化石能源为主。日益增多的人类活动不仅会加快化石燃料的消耗,还会造成大气中以CO2为主的温室气体排放量增加,打破自然界的碳平衡。